컴퓨터공학/LeetCode 1000
[LeetCode] 113. Path Sum II
saurus2
2022. 9. 28. 07:48
113. Path Sum II
Medium
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return all root-to-leaf paths where the sum of the node values in the path equals targetSum. Each path should be returned as a list of the node values, not node references.
A root-to-leaf path is a path starting from the root and ending at any leaf node. A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
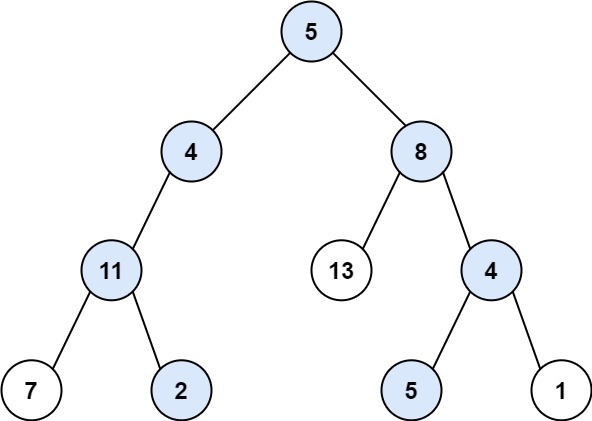
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
Output: [[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
Explanation: There are two paths whose sum equals targetSum:
5 + 4 + 11 + 2 = 22
5 + 8 + 4 + 5 = 22
Example 2:
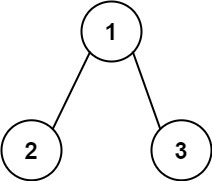
Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], targetSum = 0
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 5000].
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
- -1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
문제 풀이
- 노드의 갯수는 최대 5000 개이다.
- 재귀 호출로 풀어도 문제가 없어 보인다.
- path 를 생성해 모든 노드에 방문했을때 노드를 기록해 준다.
- 그리고 각 노드를 방문하기 전에 targetSum 과 현재값 + 노드 값을 비교하여 결과에 path 리스트를 넣는다.
- 주의할 점은 path 에 먼저 현재 노드를 넣어야한다, 그래야 정상적으로 모든 path 가 리스트에 들어간다.
- 미래의 왼/오 자식을 고려해보는게 아니라 현재 노드의 위치를 확인해보는 걸로 코드를 설계했기 때문에,
- 종료조건은 맨위에, path 입력은 두번째, 마지막으로 재귀 호출 전에 targetSum 과 비교하여 답을 구하자.
소스 코드
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
self.path = []
self.ans = []
def rec(node, total):
if not node:
return
self.path.append(node.val)
if total + node.val == targetSum:
if not node.left and not node.right:
self.ans.append(self.path.copy())
rec(node.left, total + node.val)
rec(node.right, total + node.val)
self.path.pop()
rec(root, 0)
return self.ans